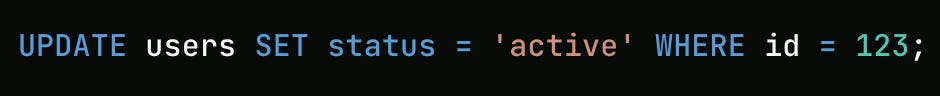What is Idempotency in Distributed Systems?
And how to Implement it
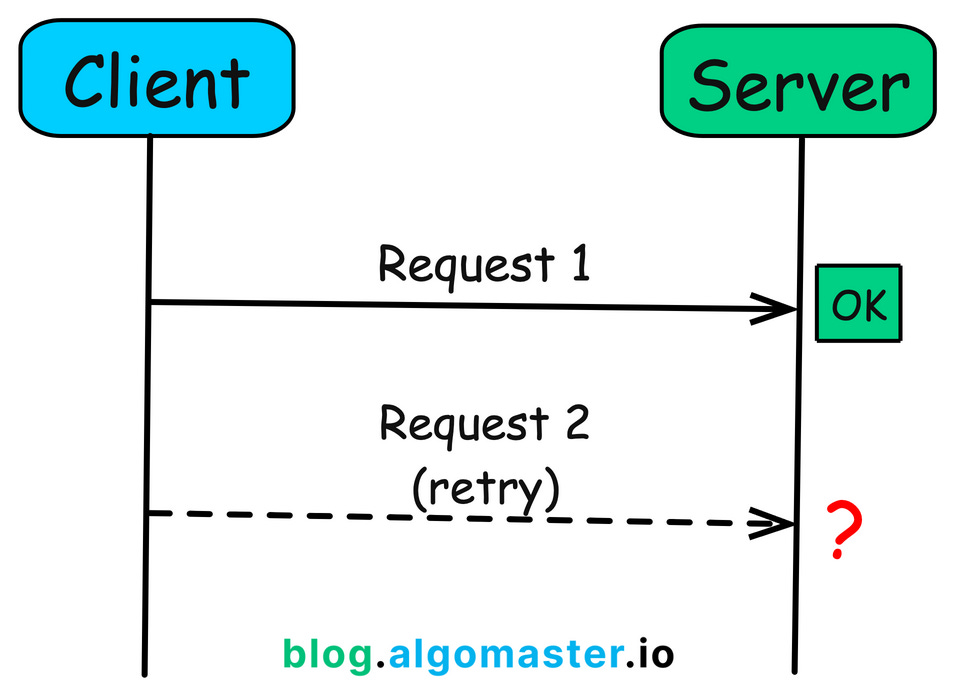
Imagine you’re making a purchase from an online store.
You hit “pay” but the screen freezes, and you’re unsure if the payment went through.
So, you refresh the page and try again.
Behind the scenes, how does the system ensure you aren’t accidentally charged twice?
This scenario highlights a common problem in distributed systems: handling repeated operations gracefully.
The solution to this problem lies in the concept of idempotency.
In this blog, we’ll explore what idempotency is, why it matters, how to implement it, challenges, considerations and best practices to ensure robust and reliable systems.
What is Idempotency?
In mathematics, an operation is idempotent if applying it multiple times produces the same result as applying it once.
For example, the absolute value function is idempotent: ||-5|| = |-5| = 5.
Idempotency is a property of certain operations whereby executing the same operation multiple times produces the same result as executing it once.
For example: If a request to delete an item is idempotent—all requests after the first will have no impact.
In programming, setting a value is idempotent, while incrementing a value is not.
Idempotent: user.status = 'active' Not Idempotent: user.login_count += 1Some operations are naturally idempotent.
No matter how many times you run this, the result remains the same.
Why Idempotency Matters
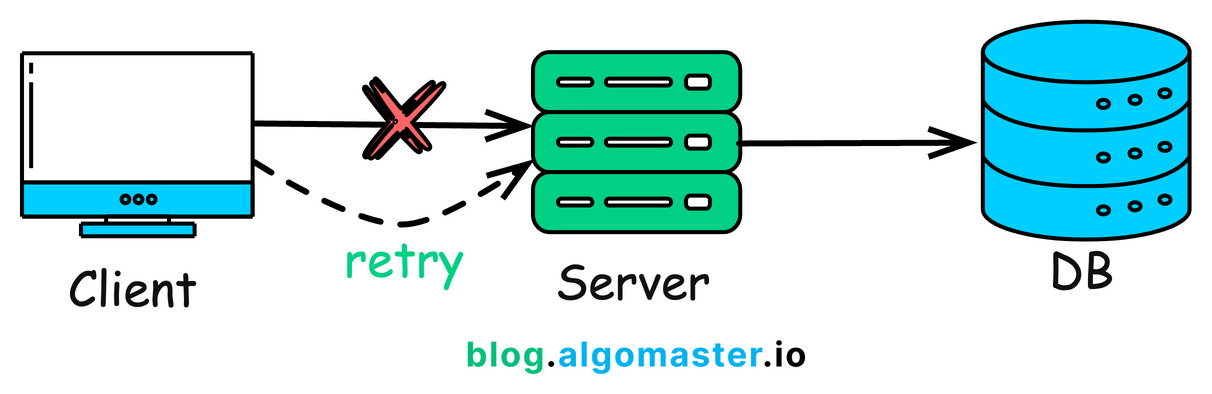
Distributed systems often require fault tolerance to ensure high availability. When a network issue causes a timeout or an error, the client might retry the request.
If the system handles retries without idempotency, every retry could change the system’s state unpredictably.
By designing operations to be idempotent, engineers create a buffer against unexpected behaviors caused by retries.
This “safety net” prevents repeated attempts from distorting the outcome, ensuring stability and reliability.
Strategies to Implement Idempotency
1. Unique Request Identifiers
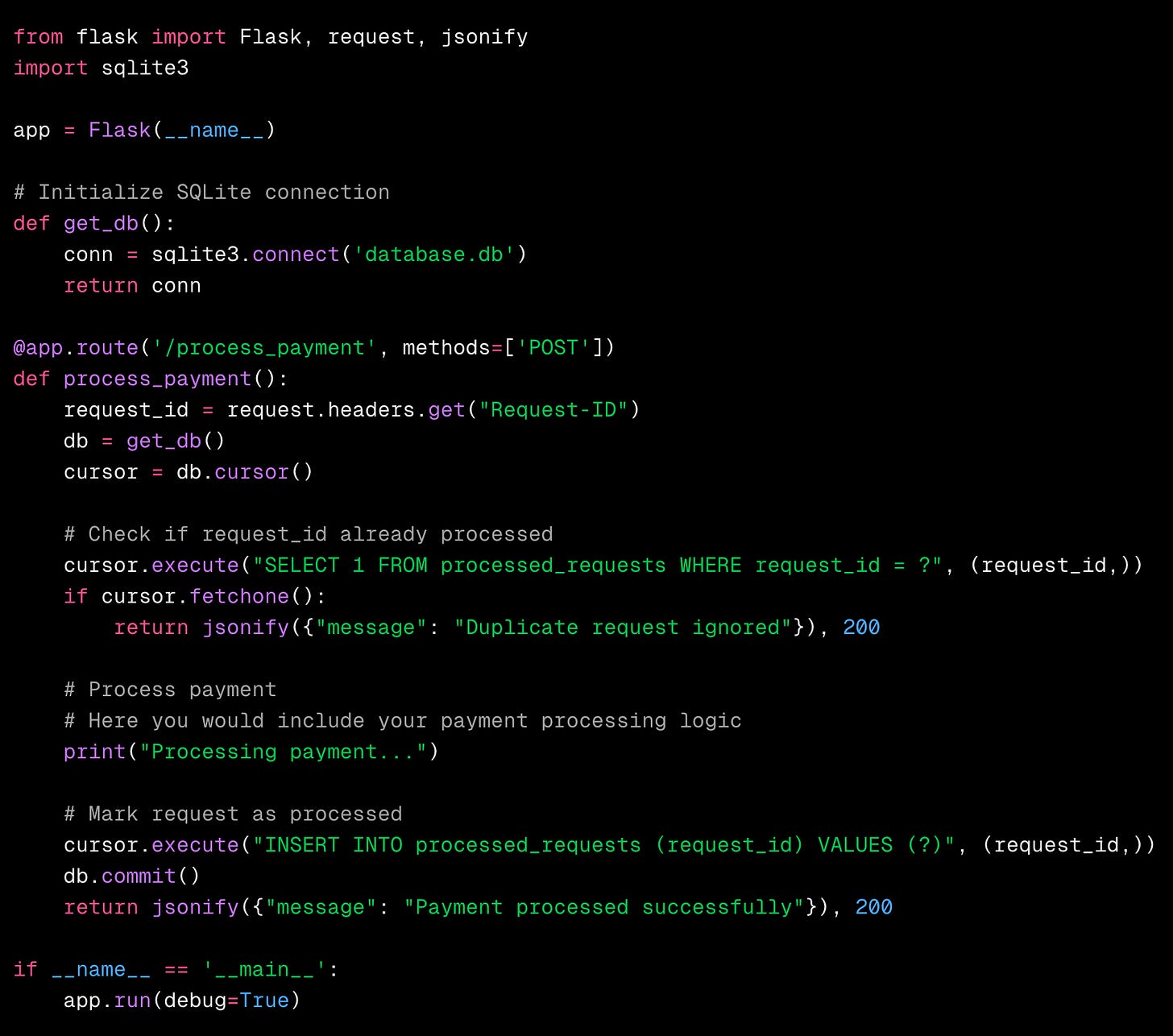
One of the simplest techniques to achieve idempotency is by attaching a unique identifier, often called an idempotency key to each request.
When a client makes a request, it generates a unique ID that the server uses to track the request. If the server receives a request with the same ID later, it knows it’s a duplicate and discards it.
Example: A payment service could require every transaction request to include a unique ID. If the client retries with the same ID, the server will skip the charge, preventing duplicate transactions.
Code Example:
In this example, each request includes a unique request_id stored in the database to track processed requests and prevent duplicates.
2. Database Design Adjustments (Upsert Operation)
Some database operations, such as inserting the same record multiple times, can lead to unintended duplicate entries.
Achieving idempotency in these cases often requires redesigning the database operations to be inherently idempotent.
This can involve using upsert operations (which updates a record if it exists or inserts it otherwise) or applying unique constraints that prevent duplicates from being added in the first place.
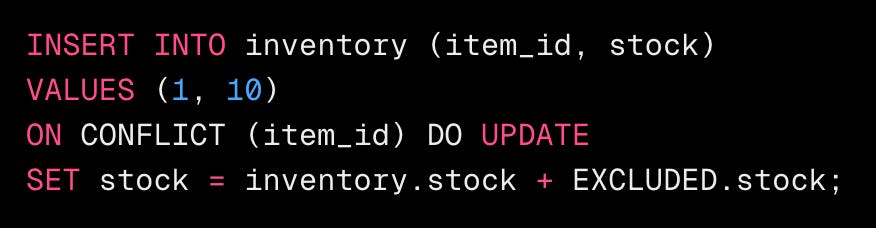
In this example, we use SQL INSERT ... ON CONFLICT to achieve an upsert operation, ensuring that duplicate entries don’t affect the database state.
This SQL statement inserts a new item if it doesn’t exist. If it does exist (conflict on item_id), it updates the stock by adding the new stock quantity, ensuring the operation remains idempotent.
3. Idempotency in Messaging Systems
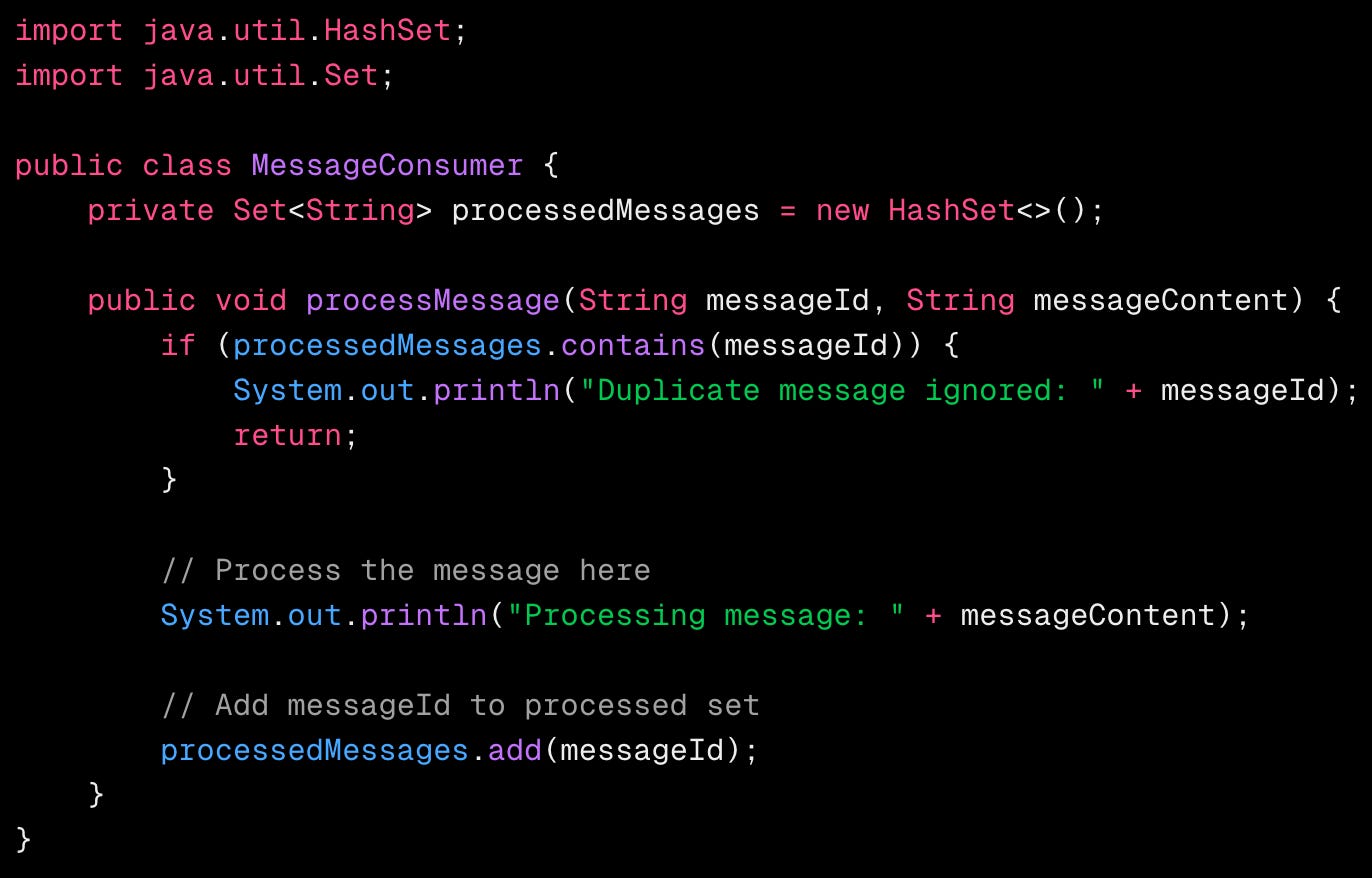
In a messaging system, we can enforce idempotency by storing a log of processed message IDs and checking against it for every incoming message.
Each message has a unique messageId. Before processing, we check if the messageId is already in processedMessages. If it is, the message is ignored; otherwise, it’s processed and added to the set to avoid duplicates.
4. Idempotency in HTTP Methods
HTTP defines several methods (verbs) for different types of requests.
These methods can be categorized by whether they are idempotent or non-idempotent, influencing how a system handles retries and preventing unintended side effects.
Idempotent Methods:
-
GET: Retrieves data from a resource. GET requests are inherently idempotent because they only read data and do not alter the server’s state.
-
Example: Accessing a blog post by making a GET request to
/posts/123will simply retrieve that post, without modifying any server data. Whether you retrieve it once or a thousand times, the post remains unchanged.
-
-
PUT: Update or completely replace an existing resource. PUT requests are idempotent because the final state is the same whether the PUT request is executed once or multiple times.
-
Example: Updating user information by making a PUT request to
/users/45with updated user details will overwrite the user’s data with the new information provided. Executing the same PUT request repeatedly results in the same final user data on the server.
-
-
DELETE: Removes a resource from the server. DELETE requests are idempotent because deleting a resource that’s already been deleted has no further effect.
-
Example: Deleting an item by making a DELETE request to
/items/678will remove the item. If you attempt the DELETE request again, it will have no effect since the item no longer exists.
-
Non-Idempotent Methods:
-
POST: Creates a new resource on the server. POST requests are non-idempotent because each request usually results in the creation of a new resource.
-
Example: Creating a new order by making a POST request to
/orderswith order details will generate a new order each time the request is made.
-
Challenges and Considerations
While idempotency is powerful, it comes with its own set of challenges:
-
Performance Overhead: Storing idempotency keys or checking for duplicate operations can add overhead and increase the overall latency.
-
State Management: Idempotency often requires maintaining state, which can be challenging in stateless architectures.
-
Distributed Systems: Ensuring idempotency across distributed systems can be challenging and may require distributed locking or consensus algorithms.
-
Time Window: How long should idempotency guarantees be maintained? Forever, or for a limited time?
-
Database Constraints: Not all operations are idempotent by default; unique constraints or upsert logic may be necessary to avoid duplication.
Best Practices
When implementing idempotency in your system, consider these best practices:
-
Use Unique Identifiers: Attach a unique ID (idempotency key) to each request to track and prevent duplicate processing.
-
Design for Idempotency from the Start: It’s much easier to design for idempotency from the beginning than to add it later.
-
Implement Retry with Backoff: When retrying idempotent operations, use an exponential backoff strategy to avoid overwhelming the system.
-
Employ Idempotent HTTP Methods: Prefer idempotent methods (GET, PUT, DELETE) for operations that may be retried; design POST with unique identifiers if idempotency is required.
-
Document Idempotent Operations: Clearly document which operations are idempotent in your API specifications.
-
Test Thoroughly: Implement tests that verify the idempotency of your operations, including edge cases and failure scenarios.
-
Use Locks or Versioning: Use locks, optimistic concurrency control, or version numbers to manage simultaneous requests safely.
Idempotency is a powerful concept in distributed systems that can greatly enhance the reliability and fault-tolerance of your systems.
Whether you’re designing a distributed database, a payment processing system, or a simple web API, considering idempotency in your design can save you (and your users) from many headaches down the road.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re finding this newsletter helpful and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every week, access to a comprehensive system design learning resource , and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish